Hurricane Matthew on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hurricane Matthew was an extremely powerful Atlantic hurricane which caused catastrophic damage and a
 On September 27, prior to Matthew becoming a tropical cyclone,
On September 27, prior to Matthew becoming a tropical cyclone,
 The Meteorological Service of Cuba raised hurricane watches for all of southeastern
The Meteorological Service of Cuba raised hurricane watches for all of southeastern
 On October 3, the governors of
On October 3, the governors of  For the fourth time in its 45-year history, the Walt Disney World Resort closed. Its theme parks, Magic Kingdom, Epcot, Disney's Hollywood Studios and Disney's Animal Kingdom, as well as water parks Disney's Blizzard Beach, Disney's Typhoon Lagoon, and Disney Springs, were closed at 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time Zone, Eastern Daylight Time on October 6, and remained closed on October 7. This was the first time since 2004 that the parks have closed, all instances due to hurricanes. Other Orlando-area theme parks, including Universal Orlando resort and SeaWorld Orlando, also closed.
The Southeastern Conference football game between LSU Tigers football, LSU and Florida Gators football, Florida, scheduled for October 8 in Gainesville, was cancelled, while the SEC football game between Georgia Bulldogs football, Georgia and South Carolina Gamecocks football, South Carolina, scheduled for October 8 in Columbia, was moved to October 9. The hurricane washed out NASCAR racing at Charlotte Motor Speedway on October 7 and 8, with the Drive for the Cure 300 race in the Xfinity Series originally scheduled for October 7 and the 2016 Bank of America 500, Bank of America 500 race in the Sprint Cup Series originally scheduled for October 8 both postponed until October 9.
On October 6, U.S. President Barack Obama declared a federal
For the fourth time in its 45-year history, the Walt Disney World Resort closed. Its theme parks, Magic Kingdom, Epcot, Disney's Hollywood Studios and Disney's Animal Kingdom, as well as water parks Disney's Blizzard Beach, Disney's Typhoon Lagoon, and Disney Springs, were closed at 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time Zone, Eastern Daylight Time on October 6, and remained closed on October 7. This was the first time since 2004 that the parks have closed, all instances due to hurricanes. Other Orlando-area theme parks, including Universal Orlando resort and SeaWorld Orlando, also closed.
The Southeastern Conference football game between LSU Tigers football, LSU and Florida Gators football, Florida, scheduled for October 8 in Gainesville, was cancelled, while the SEC football game between Georgia Bulldogs football, Georgia and South Carolina Gamecocks football, South Carolina, scheduled for October 8 in Columbia, was moved to October 9. The hurricane washed out NASCAR racing at Charlotte Motor Speedway on October 7 and 8, with the Drive for the Cure 300 race in the Xfinity Series originally scheduled for October 7 and the 2016 Bank of America 500, Bank of America 500 race in the Sprint Cup Series originally scheduled for October 8 both postponed until October 9.
On October 6, U.S. President Barack Obama declared a federal

 Large swells reached the outlying Haitian island of Île-à-Vache on October 2, prompting the evacuation of 89 people. Despite boating bans, many fishermen continued work in rough conditions. Consequently, two fishermen went missing on the morning of October 3: one near Saint-Jean-du-Sud and the other near Aquin; one was later found dead. Antecedent rainfall associated with the outer bands of Matthew triggered flooding in several towns in southern Haiti and the Dominican Republic. A person was killed when a tree fell on his home in Port Salut, while a 26-year-old man drowned while trying to rescue a child from a rushing river.
Striking the Tiburon Peninsula as a Category 4 hurricane on the morning of October 4, Matthew was the strongest storm to directly impact Haiti since Hurricane Cleo in 1964. An anemometer at Antoine-Simon Airport in Les Cayes, east of where Matthew made landfall, measured a gust of before the station went offline. Gusts in the nation's capital city of Port-au-Prince reached . Communications with areas in the direct path of Matthew were lost, and tens of thousands of people became isolated as roads and bridges were destroyed. A major bridge connecting parts of Grand'Anse (department), Grand'Anse to the rest of the country collapsed during a flash flood. 80% of
Large swells reached the outlying Haitian island of Île-à-Vache on October 2, prompting the evacuation of 89 people. Despite boating bans, many fishermen continued work in rough conditions. Consequently, two fishermen went missing on the morning of October 3: one near Saint-Jean-du-Sud and the other near Aquin; one was later found dead. Antecedent rainfall associated with the outer bands of Matthew triggered flooding in several towns in southern Haiti and the Dominican Republic. A person was killed when a tree fell on his home in Port Salut, while a 26-year-old man drowned while trying to rescue a child from a rushing river.
Striking the Tiburon Peninsula as a Category 4 hurricane on the morning of October 4, Matthew was the strongest storm to directly impact Haiti since Hurricane Cleo in 1964. An anemometer at Antoine-Simon Airport in Les Cayes, east of where Matthew made landfall, measured a gust of before the station went offline. Gusts in the nation's capital city of Port-au-Prince reached . Communications with areas in the direct path of Matthew were lost, and tens of thousands of people became isolated as roads and bridges were destroyed. A major bridge connecting parts of Grand'Anse (department), Grand'Anse to the rest of the country collapsed during a flash flood. 80% of
 Across South Carolina, at least 600,000 individuals lost power, where significant flooding was reported to have occurred in Charleston after a seawall was breached. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island experienced widespread water, sewer and power outages for several days, and the only road onto the island was not re-opened to residents until October 11. It is estimated that over 120,000 trees were downed on the island, causing extensive tree-strike damage to residences and businesses. Over 2.1 million cubic yards of vegetative debris generated by the storm was collected. The Waccamaw River crested in Conway, South Carolina, Conway at , breaking a record set by the 1928 Okeechobee hurricane. The Little Pee Dee River reached a record crest of at Galivants Ferry, South Carolina, Galivant's Ferry, also breaking a 1928 record.
Twenty-six people died in storm-related incidents across North Carolina. 680,000 in North Carolina were without power at one point. Sections of Interstate 95 Interstate 95 in South Carolina, in South Carolina and Interstate 95 in North Carolina, in North Carolina had to be shut down as a result of hurricane flooding. The North Carolina section reopened October 17. After of rain fell in Cumberland County, North Carolina, Cumberland, Harnett County, North Carolina, Harnett, Hoke County, North Carolina, Hoke, Moore County, North Carolina, Moore and Robeson County, North Carolina, Robeson Counties on September 28 causing flooding, Matthew dumped another to . As a result, the Lumber River reached a record in the south end of Lumberton, North Carolina, Lumberton, breaking the record of feet. Robeson County schools did not reopen until October 31. In Smithfield, North Carolina, Smithfield, the Neuse River crested at , higher than after Hurricane Fran. In Kinston, North Carolina, Kinston, the Neuse crested at , a foot (300 mm) higher than the record set by Hurricane Floyd. In Greenville, North Carolina, Greenville, the Tar River crested at . Preliminary estimates indicate that roughly 100,000 structures were flooded across the state and damage reached US$1.5 billion.
Across South Carolina, at least 600,000 individuals lost power, where significant flooding was reported to have occurred in Charleston after a seawall was breached. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island experienced widespread water, sewer and power outages for several days, and the only road onto the island was not re-opened to residents until October 11. It is estimated that over 120,000 trees were downed on the island, causing extensive tree-strike damage to residences and businesses. Over 2.1 million cubic yards of vegetative debris generated by the storm was collected. The Waccamaw River crested in Conway, South Carolina, Conway at , breaking a record set by the 1928 Okeechobee hurricane. The Little Pee Dee River reached a record crest of at Galivants Ferry, South Carolina, Galivant's Ferry, also breaking a 1928 record.
Twenty-six people died in storm-related incidents across North Carolina. 680,000 in North Carolina were without power at one point. Sections of Interstate 95 Interstate 95 in South Carolina, in South Carolina and Interstate 95 in North Carolina, in North Carolina had to be shut down as a result of hurricane flooding. The North Carolina section reopened October 17. After of rain fell in Cumberland County, North Carolina, Cumberland, Harnett County, North Carolina, Harnett, Hoke County, North Carolina, Hoke, Moore County, North Carolina, Moore and Robeson County, North Carolina, Robeson Counties on September 28 causing flooding, Matthew dumped another to . As a result, the Lumber River reached a record in the south end of Lumberton, North Carolina, Lumberton, breaking the record of feet. Robeson County schools did not reopen until October 31. In Smithfield, North Carolina, Smithfield, the Neuse River crested at , higher than after Hurricane Fran. In Kinston, North Carolina, Kinston, the Neuse crested at , a foot (300 mm) higher than the record set by Hurricane Floyd. In Greenville, North Carolina, Greenville, the Tar River crested at . Preliminary estimates indicate that roughly 100,000 structures were flooded across the state and damage reached US$1.5 billion.
 When the hurricane hit Virginia, Matthew caused two deaths. Heavy wind gusts of up to 68 mph and more than 11 inches of rain led to hundreds of downed trees and severe street flooding in southern Virginia Beach. The Northeast received heavy rain and minor flooding throughout the days of October 9 and 10.
When the hurricane hit Virginia, Matthew caused two deaths. Heavy wind gusts of up to 68 mph and more than 11 inches of rain led to hundreds of downed trees and severe street flooding in southern Virginia Beach. The Northeast received heavy rain and minor flooding throughout the days of October 9 and 10.
 Matthew's post-tropical remains were absorbed into a frontal zone off the coast of North Carolina. The humidity of the tropical system was drawn into the storm that was formed then. The latter gave heavy rain and strong winds in Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland from October 10 to 11.
In Nova Scotia, rain amounts were recorded from east to west as in Sydney, Nova Scotia, Sydney (Cape Breton Island), in Port Hawkesbury, in Chéticamp, Nova Scotia, Chéticamp, in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, in Kentville, and in Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Yarmouth. Heavy rains and strong winds caused flooding and dangerous conditions, particularly in the counties of Pictou, Antigonish, Guysborough and Cape Breton. Several roads were closed to heavy trucks, including Halifax Port Authority, Halifax Harbour bridges and the Confederation Bridge between New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Newfoundland was even more affected with accumulations generally ranging from in the central, southern and western areas. Steady rain fell sometimes at a rate of per hour, and even per hour in Burgeo. A private station in that community recorded a total of , while the official station of the Gander International Airport signaled .
The rain caused numerous landslides and swollen rivers cut roads. The state of emergency was declared in Lewisporte, St. Alban's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. Alban's and Little Burnt Bay. The town of St. Alban's, a community of about 1,200, was cut off from the surrounding communities when the main bridge in town was carried by the waters and a nearby community (Conne River) provided a boat to transport people to St. Alban's and out of the community. The highway to Burgeo, on the south coast of Newfoundland, was also flooded and had to be closed.
The winds of over also caused many fallen trees and electric power outages. The official maximum winds were recorded in Port aux Basques at and informally in Green Island, Fortune Bay, at . Insurance loss across Atlantic Canada were in excess of Canadian dollar, C$100 million (US$76 million).
Matthew's post-tropical remains were absorbed into a frontal zone off the coast of North Carolina. The humidity of the tropical system was drawn into the storm that was formed then. The latter gave heavy rain and strong winds in Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland from October 10 to 11.
In Nova Scotia, rain amounts were recorded from east to west as in Sydney, Nova Scotia, Sydney (Cape Breton Island), in Port Hawkesbury, in Chéticamp, Nova Scotia, Chéticamp, in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, in Kentville, and in Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Yarmouth. Heavy rains and strong winds caused flooding and dangerous conditions, particularly in the counties of Pictou, Antigonish, Guysborough and Cape Breton. Several roads were closed to heavy trucks, including Halifax Port Authority, Halifax Harbour bridges and the Confederation Bridge between New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Newfoundland was even more affected with accumulations generally ranging from in the central, southern and western areas. Steady rain fell sometimes at a rate of per hour, and even per hour in Burgeo. A private station in that community recorded a total of , while the official station of the Gander International Airport signaled .
The rain caused numerous landslides and swollen rivers cut roads. The state of emergency was declared in Lewisporte, St. Alban's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. Alban's and Little Burnt Bay. The town of St. Alban's, a community of about 1,200, was cut off from the surrounding communities when the main bridge in town was carried by the waters and a nearby community (Conne River) provided a boat to transport people to St. Alban's and out of the community. The highway to Burgeo, on the south coast of Newfoundland, was also flooded and had to be closed.
The winds of over also caused many fallen trees and electric power outages. The official maximum winds were recorded in Port aux Basques at and informally in Green Island, Fortune Bay, at . Insurance loss across Atlantic Canada were in excess of Canadian dollar, C$100 million (US$76 million).
 In Georgia, the Governor retracted previous evacuations later, emphasizing that their lives could not be endangered for those who chose not to leave. 1,000 members of the National Guard were deployed for help later.
In North Carolina, nearly 900 people had been rescued by boat crews by the morning of October 9. In April 2017, North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper requested $929 million in federal funds. The following month, the Trump administration denied more than 99 percent of this request and only provided $6.1 million to the state.
In Georgia, the Governor retracted previous evacuations later, emphasizing that their lives could not be endangered for those who chose not to leave. 1,000 members of the National Guard were deployed for help later.
In North Carolina, nearly 900 people had been rescued by boat crews by the morning of October 9. In April 2017, North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper requested $929 million in federal funds. The following month, the Trump administration denied more than 99 percent of this request and only provided $6.1 million to the state.
The NHC's advisory archive for Hurricane Matthew
* * *
EMSR186: Tropical Cyclone Matthew in Southeastern United States (delineation maps)
– Copernicus Emergency Management Service {{2016 Atlantic hurricane season buttons Hurricane Matthew, 2016 Atlantic hurricane season, Matthew 2016 in the Caribbean 2016 in Barbados 2016 in Cuba 2016 in Florida 2016 in Georgia (U.S. state) 2016 in Haiti 2016 in Martinique 2016 in North Carolina 2016 in Saint Lucia 2016 in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2016 in South Carolina 2016 in Venezuela 2016 in Virginia 2016 natural disasters Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes, Matthew Hurricanes in the Windward Islands, Matthew Hurricanes in the Caribbean Natural disasters in Haiti Hurricanes in Barbados, Matthew Hurricanes in Dominica, Matthew Hurricanes in Martinique, Matthew Hurricanes in Saint Lucia, Matthew Hurricanes in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Matthew Hurricanes in Cuba, Matthew Hurricanes in Florida, Matthew Hurricanes in Georgia (U.S. state), Matthew Hurricanes in South Carolina, Matthew Hurricanes in North Carolina, Matthew Hurricanes in Virginia, Matthews Hurricanes in Haiti, Matthew Hurricanes in the ABC Islands, Matthew Retired Atlantic hurricanes, Matthew October 2016 events in North America October 2016 events in the United States September 2016 events in North America September 2016 events in the United States 2016 natural disasters in the United States Tropical cyclones in 2016, Matthew Hurricanes in the Bahamas, Matthew
humanitarian crisis
A humanitarian crisis (or sometimes humanitarian disaster) is defined as a singular event or a series of events that are threatening in terms of health, safety or well-being of a community or large group of people. It may be an internal or extern ...
in Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, as well as widespread devastation in the southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern por ...
. The deadliest Atlantic hurricane since Hurricane Stan
Hurricane Stan was a relatively weak but deadly tropical cyclone that affected areas of Central America and Mexico in early October 2005. The eighteenth named storm and eleventh hurricane of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season, Stan formed from ...
in 2005
File:2005 Events Collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: Hurricane Katrina in the Gulf of Mexico; the Funeral of Pope John Paul II is held in Vatican City; "Me at the zoo", the first video ever to be uploaded to YouTube; Eris was discovered in ...
, and the first Category 5 Atlantic hurricane since Felix
Felix may refer to:
* Felix (name), people and fictional characters with the name
Places
* Arabia Felix is the ancient Latin name of Yemen
* Felix, Spain, a municipality of the province Almería, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, ...
in 2007, Matthew was the thirteenth named storm
Tropical cyclones and subtropical cyclones are named by various warning centers to simplify communication between forecasters and the general public regarding forecasts, watches and warnings. The names are intended to reduce confusion in the ...
, fifth hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
and second major hurricane
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
of the 2016 Atlantic hurricane season. It caused extensive damage to landmasses in the Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, and ...
, and severe damage in several islands of the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
which were still recovering from Joaquin, which had pounded the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
nearly a year earlier. Matthew also approached the southeastern United States, but stayed just offshore, paralleling the Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
coastline.
Originating from a tropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
that emerged off Africa on September 22, Matthew developed into a tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
just east of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
on September 28. It became a hurricane north of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
and Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
on September 29, before undergoing explosive intensification
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained ...
, ultimately reaching Category 5 intensity on October 1 with peak 1-minute sustained winds of 165 mph. This strength was attained at just 13.4°N latitude – the lowest latitude ever recorded for a storm of this intensity in the Atlantic basin, breaking the record set by Hurricane Ivan
Hurricane Ivan was a large, long-lived, Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread damage in the Caribbean and United States. The cyclone was the ninth named storm, the sixth hurricane and the fourth major hurricane of the active 2004 Atlan ...
in 2004. Matthew weakened slightly and fluctuated in intensity while making a northward turn toward the Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, and ...
, remaining a strong Category 4 hurricane as it made its first landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
over Haiti's Tiburon Peninsula
The Tiburon Peninsula (french: Péninsule de Tiburon), or The Xaragua Peninsula, simply "the Tiburon" (''le Tiburon''), is a region of Haiti encompassing most of Haiti's southern coast.
It starts roughly at the southernmost point of the Haiti-D ...
early on October 4, and then a second one in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
later that day. Matthew weakened somewhat but re-intensified as it tracked northwest, making landfall in the northern Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
. The storm then paralleled the coast of the southeastern United States over the next 36 hours, gradually weakening while remaining just offshore before making its fourth and final landfall over the Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge
The Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge is a 66,287 acre (267 km²) National Wildlife Refuge in southeastern South Carolina near Awendaw, South Carolina. The refuge lands and waters encompass water impoundments, creeks and bays, eme ...
near McClellanville, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
as a Category 1 hurricane on the morning of October 8. Matthew re-emerged into the Atlantic shortly afterward, eventually completing its transition into an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
as it turned away from Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands of North Carolina.
Long stretches of beach, sand dunes, marshes, and maritime forests create a unique environment where wind and waves shap ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
on October 9. The remnants of Matthew continued to accelerate towards Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
where it was absorbed by a cold front.
Widespread effects were felt from Matthew across its destructive path, however, the most significant impacts were felt in Haiti, with US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
2.8 billion in damage and 546 deaths, making Matthew the worst disaster to affect the nation since the 2010 earthquake. The combination of flooding and high winds disrupted telecommunications and destroyed extensive swaths of land; around 80% of Jérémie
Jérémie ( ht, Jeremi) is a commune and capital city of the Grand'Anse department in Haiti. It had a population of about 31,000 at the 2003 census. It is relatively isolated from the rest of the country. The Grande-Anse River flows near th ...
sustained significant damage. Four people were killed in Cuba due to a bridge collapse, and total losses in the country amounted to US$2.58 billion, most of which occurred in the Guantánamo Province. Passing through the Bahamas as a major hurricane, Matthew spread damage across several islands. Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island i ...
was hit directly, where most homes sustained damage in the townships of Eight Mile Rock and Holmes Rock. Preparations began in earnest across the southeastern United States as Matthew approached, with several states declaring states of emergencies for either entire states or coastal counties; widespread evacuations were ordered for extensive areas of the coast because of predicted high wind speeds and flooding, especially in the Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
Metropolitan Area. In Florida, over 1 million lost power as the storm passed to the east, with 478,000 losing power in Georgia and South Carolina. While damage was primarily confined to the coast in Florida and Georgia, torrential rains spread inland in the Carolinas
The Carolinas are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina, considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east.
Combining Nort ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, causing widespread flooding.
Meteorological history
A vigoroustropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
moved off the coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
on September 22 and moved rapidly across the Atlantic, being monitored by the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
(NHC) for possible tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tr ...
. Despite possessing tropical-storm winds as it approached the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
on September 27, the wave could not initially be classified as a tropical cyclone, as reconnaissance aircraft could not find a closed center. However, by 12:00 UTC on September 28, the wave developed a closed circulation while located near Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
, hence becoming a tropical storm, and was assigned the name ''Matthew''. Continuing westward under the influence of a mid-level ridge, the storm steadily intensified to attain hurricane intensity by 18:00 UTC on September 29. The effects of southwesterly wind shear unexpectedly abated late that day, and Matthew began a period of explosive intensification
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained ...
; during a 24-hour period beginning at 00:00 UTC on September 30, the cyclone's maximum winds more than doubled, from 80 mph (130 km/h) to 165 mph (270 km/h), making Matthew a Category 5 hurricane, the first since Felix
Felix may refer to:
* Felix (name), people and fictional characters with the name
Places
* Arabia Felix is the ancient Latin name of Yemen
* Felix, Spain, a municipality of the province Almería, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, ...
in 2007; the rate of intensification has only been exceeded a few times in the Atlantic since records began. Due to upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nut ...
of cooler waters, Matthew weakened to a Category 4 hurricane later on October 1, before attaining a secondary peak intensity with winds of 155 mph (250 km/h) late on October 2.
Slowly rounding the ridge, Matthew fluctuated in intensity within the Category 4 range from October 1–5. Intensification resumed again late on October 3 and culminated when Matthew made landfall near Les Anglais
Les Anglais ( ht, Zanglè), French for "The English", is a commune in the Chardonnières Arrondissement, in the Sud department of Haiti. It has 27,182 inhabitants. The eye of Hurricane Matthew made landfall near Les Anglais on 4 October ...
, Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
, around 11:00 UTC on October 4 with winds of 150 mph (240 km/h) and a pressure of , making it the strongest to hit Haiti since Cleo Cleo may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Cleo'' (magazine), an Australian magazine established in 1972, now active in Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand
* Cleo (group), a South Korean girl group formed in 1999
* ''Cleo'' (play), by Lawren ...
in 1964. Continuing northward, the hurricane struck Maisí
Maisí is a municipality and town in the Guantánamo Province of Cuba. Its administrative seat is located in the town of La Máquina.
Geography
The easternmost point of Cuba, ''Punta Maisí'' (called "Baitiquiri" by the Taino in pre-colonial tim ...
in Cuba early on October 5 as a slightly weaker storm. Cuba's and Haiti's mountainous terrain weakened Matthew to Category 3 status, as it began to accelerate northwestwards through the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
. Restrengthening occurred as Matthew's circulation became better organized, with the storm becoming a Category 4 hurricane again while passing Freeport. However, Matthew began to weaken again as an eyewall replacement cycle
In meteorology, eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones, generally with winds greater than , or major hurricanes ( Category 3 or above). When tropical cyclones reach this int ...
took place. The storm significantly weakened while closely paralleling the coasts of Florida and Georgia, the western portion of the outer eyewall came ashore in Florida as a Category 3 hurricane, while the inner eyewall remained just offshore. Matthew weakened to a Category 2 hurricane late on October 7 and then to a Category 1 hurricane by 12:00 UTC on October 8.
Around 15:00 UTC on October 8, the hurricane made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
at Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge
The Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge is a 66,287 acre (267 km²) National Wildlife Refuge in southeastern South Carolina near Awendaw, South Carolina. The refuge lands and waters encompass water impoundments, creeks and bays, eme ...
, near McClellanville, South Carolina
McClellanville is a small fishing town in rural Charleston County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 1,040 at the 2010 census. It is situated on the Atlantic coast, on land surrounded by Francis Marion National Forest, and has trad ...
, with winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) and a central pressure of , which made it the strongest to strike the United States in terms of pressure since Irene
Irene is a name derived from εἰρήνη (eirēnē), the Greek for "peace".
Irene, and related names, may refer to:
* Irene (given name)
Places
* Irene, Gauteng, South Africa
* Irene, South Dakota, United States
* Irene, Texas, United Stat ...
in 2011, and the first hurricane to make landfall north of Florida in October since Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel was the deadliest, second costliest, and most intense hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm killed at least 469 people in Haiti before striking the United States near the border between North and Sout ...
in 1954. Convection became displaced from the center as Matthew pulled away from land due to increasing wind shear, with the NHC declaring the system an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
about 200 mi (320 km) east of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina
Cape Hatteras is a cape located at a pronounced bend in Hatteras Island, one of the barrier islands of North Carolina.
Long stretches of beach, sand dunes, marshes, and maritime forests create a unique environment where wind and waves shape ...
, on October 9. The remnants persisted for another day, before they were absorbed by a cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Norther ...
.
Records
Matthew set several records during its long and destructive journey. Matthew intensified into a Category 5 hurricane at alatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
of 13.4 degrees north, breaking the record set by Ivan
Ivan () is a Slavic languages, Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John (given name), John) from Hebrew language, Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. T ...
in 2004, which had reached that intensity at a latitude of 13.7 degrees north. Matthew also maintained at least Category 4 status for the longest duration on record for the month of October, according to Phil Klotzbach of Colorado State University
Colorado State University (Colorado State or CSU) is a public land-grant research university in Fort Collins, Colorado. It is the flagship university of the Colorado State University System. Colorado State University is classified among "R1: ...
, doing so for roughly 5 days.
Preparations
Windward Islands and South America
 On September 27, prior to Matthew becoming a tropical cyclone,
On September 27, prior to Matthew becoming a tropical cyclone, LIAT
LIAT (1974) Ltd, also known as Leeward Islands Air Transport Services and operating as LIAT, is a regional airline headquartered in Antigua and Barbuda that operated high-frequency inter-island scheduled services to 15 destinations in the Caribb ...
began cancelling flights across the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
in anticipation of squally weather. Schools and businesses were closed for the duration of Matthew's passage on September 27 and 28 on Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
, St. Vincent and St. Lucia; schools in Dominica suspended classes until October 3. Hewanorra International Airport
Hewanorra International Airport , located near Vieux Fort Quarter, Saint Lucia, in the Caribbean, is the larger of Saint Lucia's two airports and is managed by the Saint Lucia Air and Seaports Authority (SLASPA). It is on the southern cape of ...
and George F. L. Charles Airport
George F. L. Charles Airport (commonly known as Vigie Airport) is the smaller of the two airports in Saint Lucia, the other being Hewanorra International Airport. It is located north of Castries, the capital city. George F. L. Charles Airport is ...
on St. Lucia were closed on September 28. Six shelters were opened across the island; 133 sought refuge in them. Upon the formation of Matthew as a tropical cyclone on September 28, governments across the Windward Islands issued tropical storm warning
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
s in anticipation of gale
A gale is a strong wind; the word is typically used as a descriptor in nautical contexts. The U.S. National Weather Service defines a gale as sustained surface winds moving at a speed of between 34 and 47 knots (, or ).tropical storm watch
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
es on September 28 for Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
, Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC i ...
, Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast ...
, and the northern coast of Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
from the Colombia–Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
border to Riohacha
Riohacha (; Wayuu: ) is a city in the Riohacha Municipality in the northern Caribbean Region of Colombia by the mouth of the Ranchería River and the Caribbean Sea. It is the capital city of the La Guajira Department. It has a sandy beach waterfr ...
. North Atlantic hurricanes affecting South America are uncommon. The watch in Colombia was later upgraded to a warning on September 30 as Matthew continued on a west-southwest track near the country. Residents across the ABC Islands were advised to board their homes and stock up on supplies, leading to long lines at supermarkets and gas stations. Curaçao's government postponed the 2016 general election until October 5. Government offices in Aruba closed for September 30. A local sporting event, the Kingdom Tournament, was canceled in Aruba. Schools across the Guajira Peninsula
The Guajira Peninsula ( es, Península de La Guajira, links=no, also spelled ''Goajira'', mainly in colonial period texts, guc, Hikükariby) is a peninsula in northern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela in the Caribbean. It is the norther ...
of Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
suspended activities for September 30. Officials opened shelters and closed beaches across the peninsula.
Jamaica
With Matthew posing a significant threat toJamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, emergency officials ordered all fishermen on the nation's cays and banks to evacuate to the mainland on September 29. The following day, Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Andrew Holness
Andrew Michael Holness, (born 22 July 1972) is a Jamaican politician who has been the Prime Minister of Jamaica since 3 March 2016, following the 2016 Jamaican general election. Holness previously served as prime minister from October 2011 to ...
held an emergency meeting regarding the hurricane and placed the government on high alert. A hurricane watch
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
was issued for the country on September 30, and later upgraded to a warning on October 1. Officials in Trelawny Parish
Trelawny (Jamaican Patois: ''Trilaani'' or ''Chrilaani'') is a parish in the county of Cornwall in northwest Jamaica. Its capital is Falmouth. It is bordered by the parishes of Saint Ann in the east, Saint James in the west, and Saint Elizab ...
placed 60 shelters on stand-by on October 2. Supermarkets were overwhelmed with residents stocking up on supplies, and many reported empty shelves and low supplies of bread, kerosene, and candles. Many people boarded up their homes and protected their property with sand bags. One hundred female prisoners were relocated from a facility in St. Catherine Parish
Saint Catherine (capital Spanish Town) is a Parishes of Jamaica, parish in the Ordinal directions, south east of Jamaica. It is located in the Counties of Jamaica, county of Middlesex, and is one of the island's largest and most economically va ...
to another in Kingston. Toll fees along Highway 2000
Highway 2000 is a highway system in Jamaica connecting Kingston, with Ocho Rios and a planned connection to Montego Bay, passing through the parishes of St. Catherine, Saint Ann, Clarendon and proposed sections through St. James, Saint Eliza ...
were to be waived during the hours before Matthew's arrival. Service at both Norman Manley International Airport
Norman Manley International Airport , formerly Palisadoes Airport, is an international airport serving Kingston, Jamaica and is located south of the island away from the centre of New Kingston. It is the second busiest airport in the country ...
and Sangster International Airport
Sangster International Airport is an international airport located east of Montego Bay, Jamaica. The airport is capable of handling nine million passengers per year. It serves as the most popular airport for tourists visiting the north coast ...
was scheduled to be suspended during the evening of October 2 or by the morning of October 3. The Jamaica Urban Transit Company
The Jamaica Urban Transit Company (JUTC) is the government owned public transport service operating within the Kingston Metropolitan Transport Region (KMTR), Spanish Town and Portmore.
The company is headquartered in Spanish Town with its prima ...
scheduled to suspend services beginning at 6:00 p.m. local time. The Jamaica Public Service informed residents that the power grid might be shut off during the storm if conditions became severe. Members of the Jamaica Defence Force
The Jamaica Defence Force (JDF) is the combined military of Jamaica, consisting of an infantry Regiment and Reserve Corps, an Air Wing, a Coast Guard fleet and a supporting Engineering Unit. The JDF is based upon the British military model, with ...
were deployed nationwide in advance of the hurricane in order to more swiftly deal with its aftermath.
Schools and government offices suspended operations starting on October 3. A total of 900 shelters opened across Jamaica and the Urban Transit Company provided buses to evacuate people from Kingston to the National Arena
Many countries have a national sport stadium, which typically serves as the primary or exclusive home for one or more of a country's national representative sports teams. The term is most often used in reference to an association football stadiu ...
. Local Minister Desmond McKenzie warned that the infrastructure of Kingston would be unable to handle the magnitude of rainfall expected. Prime Minister Andrew Holness
Andrew Michael Holness, (born 22 July 1972) is a Jamaican politician who has been the Prime Minister of Jamaica since 3 March 2016, following the 2016 Jamaican general election. Holness previously served as prime minister from October 2011 to ...
warned residents that Matthew could be more severe than Hurricane Gilbert
Hurricane Gilbert was the second most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Atlantic basin in terms of barometric pressure, only behind Hurricane Wilma in 2005. An extremely powerful tropical cyclone that formed during the 1988 Atlantic hurr ...
which devastated the nation in 1988.
Haiti
Though forecast to pass over Jamaica at the time, the large extent of tropical storm-force winds prompted the issuance of a tropical storm watch forHaiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
's Tiburon Peninsula
The Tiburon Peninsula (french: Péninsule de Tiburon), or The Xaragua Peninsula, simply "the Tiburon" (''le Tiburon''), is a region of Haiti encompassing most of Haiti's southern coast.
It starts roughly at the southernmost point of the Haiti-D ...
toward the border with the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
. Following an eastward shift in Matthew's predicted track, a hurricane watch was issued for much of Haiti on October 1, encompassing areas from Môle-Saint-Nicolas
Môle-Saint-Nicolas (; ht, Mòlsennikola or ) is a commune in the north-western coast of Haiti. It is the chief town of the Môle-Saint-Nicolas Arrondissement in the department of Nord-Ouest.
History
Christopher Columbus' first voyage to ...
south to the Dominican Republic border; this was upgraded to a warning just hours later. The warning eventually encompassed the entire country by the afternoon of October 2. Residents on outlying islands of Haiti were evacuated to the mainland. Life-threatening rainfall was forecast to affect much of the nation, with accumulations averaging along the southern coast with isolated peaks up to . Although government officials held meetings on storm preparation, Radio France Internationale
Radio France Internationale, usually referred to as RFI, is the state-owned international radio broadcaster of France. With 37.2 million listeners in 2014, it is one of the most-listened-to international radio stations in the world, along with ...
reported that Haiti does not have the logistical capability to handle a large-scale disaster. Only 576 shelters, with a collective capacity of 90,000 people, were listed for all of southern Haiti. According to the International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers.
The IOM was ...
, 55,107 internally displaced person
An internally displaced person (IDP) is someone who is forced to leave their home but who remains within their country's borders. They are often referred to as refugees, although they do not fall within the legal definitions of a refugee.
...
s remained in camps or hosting sites without adequate protection from the hurricane.
Provisional President of Haiti Jocelerme Privert
Jocelerme Privert (; born 1 February 1953) is a Haitian accountant and bureaucrat who served as the interim President of Haiti from 2016 to 2017.
Political career
Early political career
A longtime politician, he first served as the economics ...
addressed the nation on October 2, urging those living along the coast and in poorly constructed homes to evacuate and comply with authorities. Despite pleas from officials, many residents refused to leave their homes. Schools were closed for October 3–4, though government offices remained open. Nationwide, a total of 1,300 shelters were readied with a total capacity of 390,000 people. More than 18,000 volunteers and members of the Red Cross, community intervention teams, municipal committees, and local emergency services were readied to assist residents. At least 500 people were evacuated from Jérémie
Jérémie ( ht, Jeremi) is a commune and capital city of the Grand'Anse department in Haiti. It had a population of about 31,000 at the 2003 census. It is relatively isolated from the rest of the country. The Grande-Anse River flows near th ...
. Although civil protection officials took to the streets to warn people, many residents were unaware that Matthew was even approaching the country a day before its expected landfall. Evacuations continued through the hurricane's landfall with the total number of people in shelters reaching 9,280 by 2:00 a.m. local time on October 4.
On October 5, the Electoral Provisional Council postponed the presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, the second round of the legislative elections and the first round of the Senate elections until November 20.
Dominican Republic
On the morning of October 2, a tropical storm warning was raised for the southern coast of the Dominican Republic from Barahona west to the Haitian border, and a tropical storm watch was issued for the northern coast from Puerto Plata west to the Haitian border. At least 8,500 people were evacuated in southwestern areas of the country by the morning of October 3.Cuba and the Bahamas
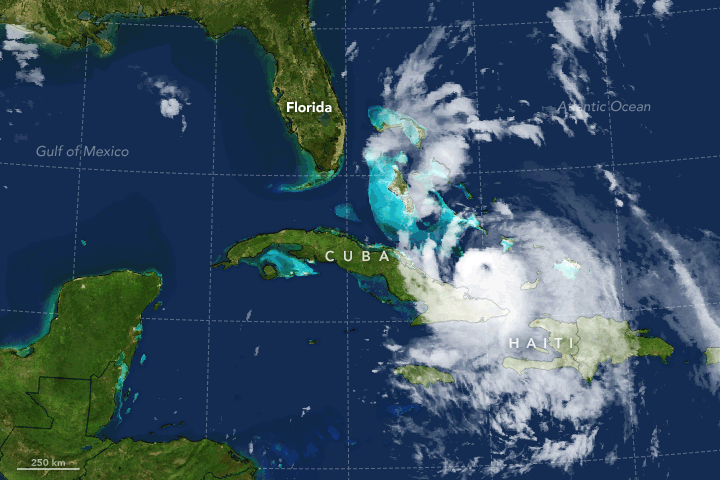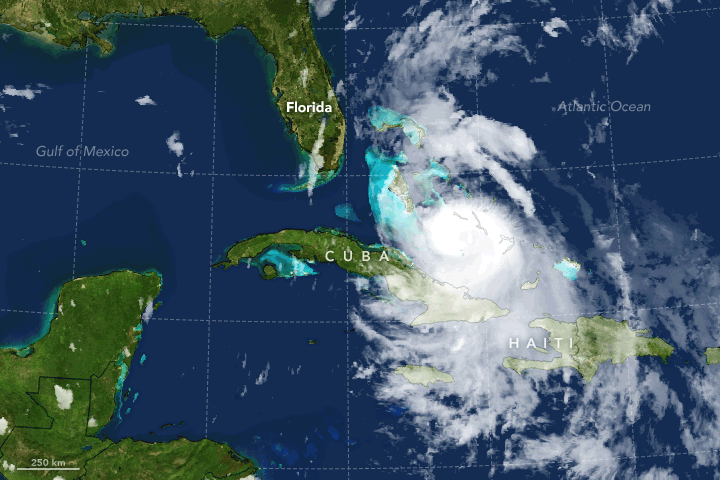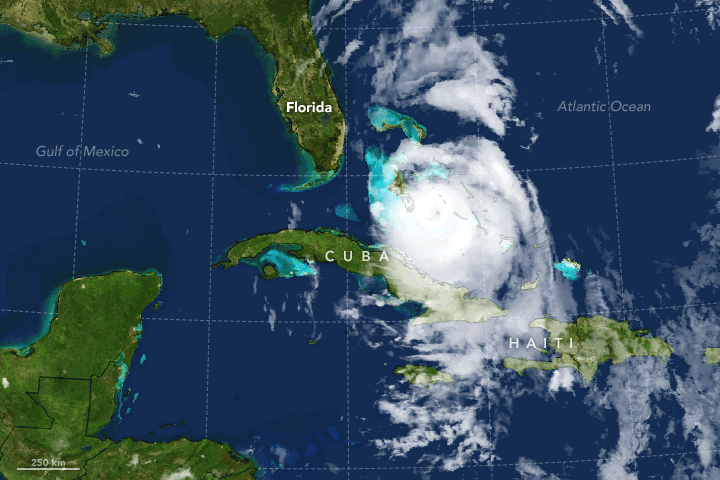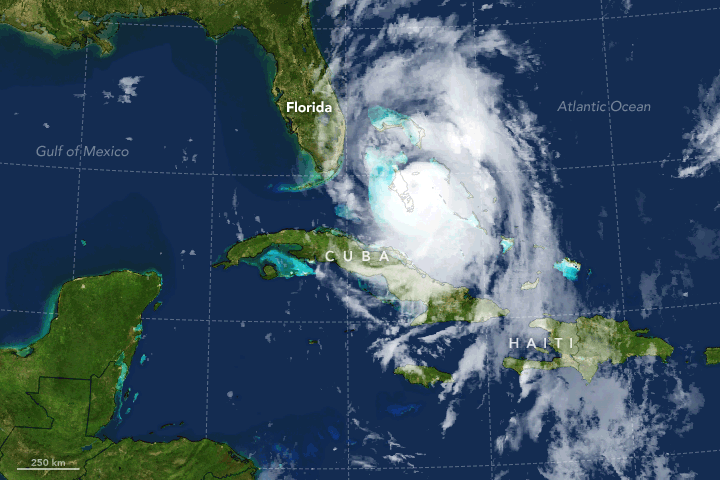
 The Meteorological Service of Cuba raised hurricane watches for all of southeastern
The Meteorological Service of Cuba raised hurricane watches for all of southeastern Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
on October 1, encompassing the provinces of Camagüey
Camagüey () is a city and municipality in central Cuba and is the nation's third-largest city with more than 321,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of the Camagüey Province.
It was founded as Santa María del Puerto del Príncipe in 1514, by S ...
, Las Tunas, Granma, Holguín
Holguín () is a municipality and city in Cuba, and the capital of Province of Holguín. After Havana, Santiago de Cuba, and Camagüey, it is the fourth largest city in Cuba.
History
Before Columbus, the Taino people settled in huts made fro ...
, Santiago de Cuba
Santiago de Cuba is the second-largest city in Cuba and the capital city of Santiago de Cuba Province. It lies in the southeastern area of the island, some southeast of the Cuban capital of Havana.
The municipality extends over , and contains t ...
, and Guantánamo
Guantánamo (, , ) is a municipality and city in southeast Cuba and capital of Guantánamo Province.
Guantánamo is served by the Caimanera port near the site of a U.S. naval base. The area produces sugarcane and cotton wool. These are traditi ...
. This was subsequently upgraded to a warning on October 2 for all provinces except Camagüey. Non-essential personnel in the United States' Guantanamo Bay Naval Base
Guantanamo Bay Naval Base ( es, Base Naval de la Bahía de Guantánamo), officially known as Naval Station Guantanamo Bay or NSGB, (also called GTMO, pronounced Gitmo as jargon by members of the U.S. military) is a United States military bas ...
began evacuations that day. Evacuations of more than 1 million people across Cuba started that morning, including 252,000 in Santiago de Cuba, and 230,000 from Las Tunas with priority placed on those along the coast. Across Santiago de Cuba, which suffered extensive damage from Hurricane Sandy
Hurricane Sandy (unofficially referred to as ''Superstorm Sandy'') was an extremely destructive and strong Atlantic hurricane, as well as the largest Atlantic hurricane on record as measured by diameter, with tropical-storm-force winds spann ...
in 2012, 218 shelters were opened and officials placed extra attention on Socapa, Caracoles, and Cayo Granma. Emergency personnel, primarily doctors, were dispatched to high-risk areas and supplies were stockpiled.
The Government of the Bahamas began issuing hurricane watches on October 2 for southeastern islands as well as the Turks and Caicos
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and n ...
. Flights across southern islands were cancelled and schools suspended operations beginning the following day.
United States
 On October 3, the governors of
On October 3, the governors of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
declared a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
. The next day, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
governor Nikki Haley ordered an evacuation for those residents living within one hundred miles (160 km) of the coast. Interstate 26 in South Carolina
Interstate 26 (I-26) is a South Carolina Interstate highway running generally east–west from near Landrum, in Spartanburg County, to U.S. Route 17 (US 17), in Charleston, South Carolina. It is also the longest Interstate Highwa ...
eastbound between the coast and Columbia was reversed on Wednesday to facilitate movement away from the Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an impor ...
and Charleston areas. Evacuations of Cape Lookout National Seashore
Cape Lookout National Seashore preserves a 56-mile (90-km) long section of the Southern Outer Banks, or Crystal Coast, of North Carolina, USA, running from Ocracoke Inlet on the northeast to Beaufort Inlet on the southeast. Three undeveloped barrie ...
in North Carolina began this day as well. By October 4, North Carolina Governor Pat McCrory
Patrick Lloyd McCrory (born October 17, 1956) is an American businessman, politician and radio host who served as the 74th governor of North Carolina from 2013 to 2017. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as the 53rd Mayor ...
had ordered that evacuation be mandatory. A state of emergency was also declared for 13 counties in eastern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
.
On October 5, Port Canaveral
Port Canaveral is a cruise, cargo, and naval port in Brevard County, Florida, United States. It is one of the busiest cruise ports in the world with 4.5 million cruise passengers passing through during 2016. Over 5.4 million tonnes of bulk car ...
was closed by the U.S. Coast Guard, the first closure since 2004. Eight cruise ships and four cargo ships were scheduled to visit the port between October 5–9. On Cape Canaveral, home to both civilian and military spaceflight facilities, no rockets or spacecraft were in vulnerable positions; at the time of Matthew's approach, the next launch was scheduled for November 4. The Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968 ...
began preparations of the facilities on October 5. Older buildings at the KSC were designed to withstand winds of ; buildings constructed after 1992, when Category 5 Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a very powerful and destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It is the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures damaged ...
struck the Miami area, are built to withstand winds. At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the U.S. Air Force's 45th Space Wing began disconnecting electric power to non-essential facilities on October 4.
 For the fourth time in its 45-year history, the Walt Disney World Resort closed. Its theme parks, Magic Kingdom, Epcot, Disney's Hollywood Studios and Disney's Animal Kingdom, as well as water parks Disney's Blizzard Beach, Disney's Typhoon Lagoon, and Disney Springs, were closed at 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time Zone, Eastern Daylight Time on October 6, and remained closed on October 7. This was the first time since 2004 that the parks have closed, all instances due to hurricanes. Other Orlando-area theme parks, including Universal Orlando resort and SeaWorld Orlando, also closed.
The Southeastern Conference football game between LSU Tigers football, LSU and Florida Gators football, Florida, scheduled for October 8 in Gainesville, was cancelled, while the SEC football game between Georgia Bulldogs football, Georgia and South Carolina Gamecocks football, South Carolina, scheduled for October 8 in Columbia, was moved to October 9. The hurricane washed out NASCAR racing at Charlotte Motor Speedway on October 7 and 8, with the Drive for the Cure 300 race in the Xfinity Series originally scheduled for October 7 and the 2016 Bank of America 500, Bank of America 500 race in the Sprint Cup Series originally scheduled for October 8 both postponed until October 9.
On October 6, U.S. President Barack Obama declared a federal
For the fourth time in its 45-year history, the Walt Disney World Resort closed. Its theme parks, Magic Kingdom, Epcot, Disney's Hollywood Studios and Disney's Animal Kingdom, as well as water parks Disney's Blizzard Beach, Disney's Typhoon Lagoon, and Disney Springs, were closed at 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time Zone, Eastern Daylight Time on October 6, and remained closed on October 7. This was the first time since 2004 that the parks have closed, all instances due to hurricanes. Other Orlando-area theme parks, including Universal Orlando resort and SeaWorld Orlando, also closed.
The Southeastern Conference football game between LSU Tigers football, LSU and Florida Gators football, Florida, scheduled for October 8 in Gainesville, was cancelled, while the SEC football game between Georgia Bulldogs football, Georgia and South Carolina Gamecocks football, South Carolina, scheduled for October 8 in Columbia, was moved to October 9. The hurricane washed out NASCAR racing at Charlotte Motor Speedway on October 7 and 8, with the Drive for the Cure 300 race in the Xfinity Series originally scheduled for October 7 and the 2016 Bank of America 500, Bank of America 500 race in the Sprint Cup Series originally scheduled for October 8 both postponed until October 9.
On October 6, U.S. President Barack Obama declared a federal state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
for Florida, later extending to include Georgia and South Carolina. Florida's governor Rick Scott urged over 1.5 million people to evacuate, with Hurricane Matthew expected to make landfall by the evening of that day. Several News presenter, news anchors also issued dire warnings urging Floridians to evacuate.
That same day, Georgia governor Nathan Deal ordered a mandatory evacuation for all areas of the state east of Interstate 95 in Georgia, Interstate 95, and the Georgia Department of Public Safety reversed the eastbound lanes on a portion of Interstate 16 effective until the following day.
Online response
On October 6, the Conservatism in the United States, conservative news aggregator ''Drudge Report''—run by Matt Drudge—headlined a five-word comment on Matthew: "Storm Fizzle? Matthew Looks Ragged!" which linked to a ''Miami Herald'' article. Drudge later used Twitter to claim that the National Hurricane Center was lying to the public about the intensity of the storm, stating that measurements from Nassau, Bahamas, did not match the 165 mph (270 km/h) gusts listed in public advisories. The tweets implied that the hurricane was not as dangerous as it seemed and that politicians were trying to "Global warming conspiracy theory, blame mankind," referring to a blog posting about Hillary Clinton. This came on the heels of radio talk show host Rush Limbaugh's claims of the conspiracy to "sell" climate change. The claims of conspiracy were posted as Matthew posed a dire threat to Florida's east coast and when residents across the state were being urged to evacuate immediately. Drudge's commentary was quickly met with sharp condemnation and criticism from meteorologists and public officials. Democratic United States House of Representatives, Representative Keith Ellison called the comments "irresponsible" and urged people to "not listen to this man." Jason Samenow of ''The Washington Post'' described it as an "incredible and offensive accusation", and stated that it "may have introduced enough doubt to lead [residents] into a decision they will regret."Impact
Windward Islands
On Saint Vincent (Antilles), St. Vincent heavy rains caused landslides and flooding across the island. One person was killed in the town of Layou when a boulder broke loose. In nearby Buccament Bay, a river overtopped its banks, prompting at least 25 people to evacuate to emergency shelters. The Hermitage River rose by at least in one hour, and as a precautionary measure, the Central Water and Sewage Authority shut off all water service. Flooding also took place in Vermont, South Rivers, sections of Kingstown, Campden Park, Arnos Vale, and Langley Park. Debris deposited by flooded rivers rendered many roads impassable. Strong winds in excess of downed many trees and power lines on St. Lucia, leaving roughly 70 percent of the island without power. Landslides and flooding, the result of more than of rain accompanying the storm, damaged many homes and roads. Rainfall at Hewanorra International Airport amounted to . The nation's banana crop suffered significant damage; 85 percent of farms reported losses. Two homes were destroyed, one in Bisee, and one in Gros Islet; several others were damaged. Roads in Castries, Gros-Islet, Dennery, and Soufriere became impassible from debris or landslides. Some damage was also reported on Dominica, temporarily leaving many people without water and electricity. Heavy rainfall in Grenada disrupted the water supply in multiple communities. In Martinique strong winds, which gusted up to in Saint-Pierre, Martinique, Saint-Pierre, wreaked havoc on the power grid; roughly 55,000 people lost electricity. Numerous trees downed by the winds blocked roadways while heavy rains led to flooding. The main road from Fort-de-France to southern towns was rendered impassable during the storm. Approximately 4,000 people lost their water supply. Three people sustained minor injuries.ABC islands and South America
The effects of Matthew across the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands were relatively limited despite its proximity. Some street flooding occurred on Aruba and Curaçao. Heavy winds were also experienced. There was some damage to cars after street flooding occurred. Outdoor bars and restaurants were damaged. The Guajira Peninsula of Colombia saw its first heavy rain event in three years, leading to widespread flash flooding. One person drowned in a swollen river in Uribia, La Guajira, Uribia; of rain fell in 30 minutes in the town. Rainfall in Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena reached during a 24-hour span and Santa Marta saw . Along coastal areas of the peninsula, large swells damaged buildings, prompting the evacuation of 380 people in Manaure, La Guajira, Manaure. Roughly 70 percent of Tucurinca flooded when the Magdalena River overtopped its banks; a nearby bridge collapsed, isolating some communities. Approximately 73,000 people were affected by the floods. The dangerous conditions produced by Matthew prevented thousands of people from voting in a 2016 Colombian peace agreement referendum, peace agreement referendum.Jamaica
Jamaica suffered relatively minor effects, characteristic of tropical storm conditions. Along the coast, rip currents and Coastal erosion, beach erosion was reported, with additional flooding due to rainfall occurring. Strong wind gusts tore at the island's vegetation, causing minor damage.Haiti

 Large swells reached the outlying Haitian island of Île-à-Vache on October 2, prompting the evacuation of 89 people. Despite boating bans, many fishermen continued work in rough conditions. Consequently, two fishermen went missing on the morning of October 3: one near Saint-Jean-du-Sud and the other near Aquin; one was later found dead. Antecedent rainfall associated with the outer bands of Matthew triggered flooding in several towns in southern Haiti and the Dominican Republic. A person was killed when a tree fell on his home in Port Salut, while a 26-year-old man drowned while trying to rescue a child from a rushing river.
Striking the Tiburon Peninsula as a Category 4 hurricane on the morning of October 4, Matthew was the strongest storm to directly impact Haiti since Hurricane Cleo in 1964. An anemometer at Antoine-Simon Airport in Les Cayes, east of where Matthew made landfall, measured a gust of before the station went offline. Gusts in the nation's capital city of Port-au-Prince reached . Communications with areas in the direct path of Matthew were lost, and tens of thousands of people became isolated as roads and bridges were destroyed. A major bridge connecting parts of Grand'Anse (department), Grand'Anse to the rest of the country collapsed during a flash flood. 80% of
Large swells reached the outlying Haitian island of Île-à-Vache on October 2, prompting the evacuation of 89 people. Despite boating bans, many fishermen continued work in rough conditions. Consequently, two fishermen went missing on the morning of October 3: one near Saint-Jean-du-Sud and the other near Aquin; one was later found dead. Antecedent rainfall associated with the outer bands of Matthew triggered flooding in several towns in southern Haiti and the Dominican Republic. A person was killed when a tree fell on his home in Port Salut, while a 26-year-old man drowned while trying to rescue a child from a rushing river.
Striking the Tiburon Peninsula as a Category 4 hurricane on the morning of October 4, Matthew was the strongest storm to directly impact Haiti since Hurricane Cleo in 1964. An anemometer at Antoine-Simon Airport in Les Cayes, east of where Matthew made landfall, measured a gust of before the station went offline. Gusts in the nation's capital city of Port-au-Prince reached . Communications with areas in the direct path of Matthew were lost, and tens of thousands of people became isolated as roads and bridges were destroyed. A major bridge connecting parts of Grand'Anse (department), Grand'Anse to the rest of the country collapsed during a flash flood. 80% of Jérémie
Jérémie ( ht, Jeremi) is a commune and capital city of the Grand'Anse department in Haiti. It had a population of about 31,000 at the 2003 census. It is relatively isolated from the rest of the country. The Grande-Anse River flows near th ...
, along the north shore of the Tiburon Peninsula, suffered tremendous damage; homes were flattened and medical facilities suffered major damage. A radio host in Port-au-Prince stated that Jérémie was "pretty much wiped out from the seaboard all the way to the cathedral".
Officially, 546 deaths were attributed to the storm in Haiti, however local governments believed the death toll to be over 1,000; this value may have been overestimated. According to the nation's Civil Protection Directorate, the death toll was 546 as of October 14, with 128 people missing and 439 injured. The government initially estimated damages at around 124 billion gourdes (US$1.9 billion), but later research found that the actual damages were up to $2.8 billion. Approximately 2.1 million people were affected by the storm, of whom 1.4 million (12 percent of Haiti's population) were left in need of assistance. Furthermore, roughly 175,000 people were left homeless.
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic reported significant rainfall and coastal flooding due to Matthew. An automated weather station in Cabo Rojo, Dominican Republic, Cabo Rojo measured of rain by the afternoon of October 3. Four people died after a house collapsed on top of them. Damage of the flooding were about Dominican peso, RD$20 billion (US$434 million).Cuba
Coastal flooding began in Granma Province, Cuba, on October 2, affecting three towns along the Sierra Maestras. Hurricane Matthew struck the easternmost province of Cuba during the evening of October 4 as a Category 4, causing tremendous damage. The coastal city of Baracoa suffered widespread damage from violent winds, and storm surge, the latter of which gutted countless buildings. Despite the severity of damage, no fatalities were reported in the city. A communication tower in Majayara collapsed during the storm and a bridge spanning the Toa river was destroyed; several communities left isolated as a result. Damages in Cuba amounted to US$2.58 billion; most of which occurred in the Guantánamo Province. Nearly two months later, on November 22, a municipal bridge in the city of Moa, Cuba, Moa that was damaged by Hurricane Matthew collapsed, killing four employees of Canadian mining company Sherritt International. The employees were undertaking repairs to restore access between Moa and a mining site.Bahamas
Experiencing a direct hit from the eyewall of Matthew,Grand Bahama
Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of the Bahamas, with the town of West End located east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in the Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island i ...
suffered extensive damage. An estimated 95 percent of homes in Eight Mile Rock and Holmes Rock sustained severe damage. Numerous trees and power lines were toppled by the storm's high winds, rendering roads impassable. Flooding-induced by the backside of the storm affected much of the western half of the island. Total losses from Matthew in the Bahamas are estimated to be around $580 million.
United States
In total, the storm killed 47 people in the US, including 26 in North Carolina, 12 in Florida, 3 in Georgia, 4 in South Carolina, and 2 in Virginia. According to the National Centers for Environmental Information, damage from Matthew across the United States reached approximately $10 billion. This ranked it the costliest national disaster in the country for 2016 alongside 2016 Louisiana floods, record floods in Louisiana.Florida and Georgia
As Hurricane Matthew traveled rapidly towards the southeastern region of the United States, it hit closely to the coasts of Florida, South Carolina, Georgia, and North Carolina. On October 7 in Fernandina Beach, Florida, there was a peak surge of above normal. Additionally, in the St. Augustine area, water was reported to be above ground. As Matthew tracked parallel to the Florida coast, it left over one million people without power across the state of Florida. In Jacksonville, Florida, Jacksonville it caused major sand dune damage and flooding in the St. Johns River. It also destroyed many properties and knocked out power for nearly 250,000 electrical customers. In Indialantic, Florida, firefighters exposed themselves to the storm's winds to put out a fire, which reportedly destroyed a greenhouse. In Florida, one woman died due to a heart attack; she had called for aid, but medical services were not able to arrive due to Matthew's high winds. Another two women were killed by falling trees. In the Flagler Beach area, a portion of Florida State Road A1A was washed away. AtKennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968 ...
, winds reached at ground level while a gust of was observed atop a tower. The facility suffered several million dollars-worth of damage, though overall impacts were less than anticipated. The roof of Operations Support Building II broke, and rainwater damaged the interior. Air conditioning was lost throughout Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39, Launch Complex 39 as well. The planned launches of GOES-R, NOAA's next generation weather satellite, and CYGNSS, a cluster of smaller satellites which study hurricanes, were delayed due to the suspension of operations during Matthew.
Over 250,000 customers were left without power in Georgia after Hurricane Matthew affected the area. Roads were also blocked in the Brunswick, Georgia, area, where all access points to St. Simons, Georgia, St. Simons Island were rendered impassable.
North and South Carolina
 Across South Carolina, at least 600,000 individuals lost power, where significant flooding was reported to have occurred in Charleston after a seawall was breached. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island experienced widespread water, sewer and power outages for several days, and the only road onto the island was not re-opened to residents until October 11. It is estimated that over 120,000 trees were downed on the island, causing extensive tree-strike damage to residences and businesses. Over 2.1 million cubic yards of vegetative debris generated by the storm was collected. The Waccamaw River crested in Conway, South Carolina, Conway at , breaking a record set by the 1928 Okeechobee hurricane. The Little Pee Dee River reached a record crest of at Galivants Ferry, South Carolina, Galivant's Ferry, also breaking a 1928 record.
Twenty-six people died in storm-related incidents across North Carolina. 680,000 in North Carolina were without power at one point. Sections of Interstate 95 Interstate 95 in South Carolina, in South Carolina and Interstate 95 in North Carolina, in North Carolina had to be shut down as a result of hurricane flooding. The North Carolina section reopened October 17. After of rain fell in Cumberland County, North Carolina, Cumberland, Harnett County, North Carolina, Harnett, Hoke County, North Carolina, Hoke, Moore County, North Carolina, Moore and Robeson County, North Carolina, Robeson Counties on September 28 causing flooding, Matthew dumped another to . As a result, the Lumber River reached a record in the south end of Lumberton, North Carolina, Lumberton, breaking the record of feet. Robeson County schools did not reopen until October 31. In Smithfield, North Carolina, Smithfield, the Neuse River crested at , higher than after Hurricane Fran. In Kinston, North Carolina, Kinston, the Neuse crested at , a foot (300 mm) higher than the record set by Hurricane Floyd. In Greenville, North Carolina, Greenville, the Tar River crested at . Preliminary estimates indicate that roughly 100,000 structures were flooded across the state and damage reached US$1.5 billion.
Across South Carolina, at least 600,000 individuals lost power, where significant flooding was reported to have occurred in Charleston after a seawall was breached. Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, Hilton Head Island experienced widespread water, sewer and power outages for several days, and the only road onto the island was not re-opened to residents until October 11. It is estimated that over 120,000 trees were downed on the island, causing extensive tree-strike damage to residences and businesses. Over 2.1 million cubic yards of vegetative debris generated by the storm was collected. The Waccamaw River crested in Conway, South Carolina, Conway at , breaking a record set by the 1928 Okeechobee hurricane. The Little Pee Dee River reached a record crest of at Galivants Ferry, South Carolina, Galivant's Ferry, also breaking a 1928 record.
Twenty-six people died in storm-related incidents across North Carolina. 680,000 in North Carolina were without power at one point. Sections of Interstate 95 Interstate 95 in South Carolina, in South Carolina and Interstate 95 in North Carolina, in North Carolina had to be shut down as a result of hurricane flooding. The North Carolina section reopened October 17. After of rain fell in Cumberland County, North Carolina, Cumberland, Harnett County, North Carolina, Harnett, Hoke County, North Carolina, Hoke, Moore County, North Carolina, Moore and Robeson County, North Carolina, Robeson Counties on September 28 causing flooding, Matthew dumped another to . As a result, the Lumber River reached a record in the south end of Lumberton, North Carolina, Lumberton, breaking the record of feet. Robeson County schools did not reopen until October 31. In Smithfield, North Carolina, Smithfield, the Neuse River crested at , higher than after Hurricane Fran. In Kinston, North Carolina, Kinston, the Neuse crested at , a foot (300 mm) higher than the record set by Hurricane Floyd. In Greenville, North Carolina, Greenville, the Tar River crested at . Preliminary estimates indicate that roughly 100,000 structures were flooded across the state and damage reached US$1.5 billion.
Virginia and the Northeast
 When the hurricane hit Virginia, Matthew caused two deaths. Heavy wind gusts of up to 68 mph and more than 11 inches of rain led to hundreds of downed trees and severe street flooding in southern Virginia Beach. The Northeast received heavy rain and minor flooding throughout the days of October 9 and 10.
When the hurricane hit Virginia, Matthew caused two deaths. Heavy wind gusts of up to 68 mph and more than 11 inches of rain led to hundreds of downed trees and severe street flooding in southern Virginia Beach. The Northeast received heavy rain and minor flooding throughout the days of October 9 and 10.
Canada
 Matthew's post-tropical remains were absorbed into a frontal zone off the coast of North Carolina. The humidity of the tropical system was drawn into the storm that was formed then. The latter gave heavy rain and strong winds in Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland from October 10 to 11.
In Nova Scotia, rain amounts were recorded from east to west as in Sydney, Nova Scotia, Sydney (Cape Breton Island), in Port Hawkesbury, in Chéticamp, Nova Scotia, Chéticamp, in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, in Kentville, and in Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Yarmouth. Heavy rains and strong winds caused flooding and dangerous conditions, particularly in the counties of Pictou, Antigonish, Guysborough and Cape Breton. Several roads were closed to heavy trucks, including Halifax Port Authority, Halifax Harbour bridges and the Confederation Bridge between New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Newfoundland was even more affected with accumulations generally ranging from in the central, southern and western areas. Steady rain fell sometimes at a rate of per hour, and even per hour in Burgeo. A private station in that community recorded a total of , while the official station of the Gander International Airport signaled .
The rain caused numerous landslides and swollen rivers cut roads. The state of emergency was declared in Lewisporte, St. Alban's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. Alban's and Little Burnt Bay. The town of St. Alban's, a community of about 1,200, was cut off from the surrounding communities when the main bridge in town was carried by the waters and a nearby community (Conne River) provided a boat to transport people to St. Alban's and out of the community. The highway to Burgeo, on the south coast of Newfoundland, was also flooded and had to be closed.
The winds of over also caused many fallen trees and electric power outages. The official maximum winds were recorded in Port aux Basques at and informally in Green Island, Fortune Bay, at . Insurance loss across Atlantic Canada were in excess of Canadian dollar, C$100 million (US$76 million).
Matthew's post-tropical remains were absorbed into a frontal zone off the coast of North Carolina. The humidity of the tropical system was drawn into the storm that was formed then. The latter gave heavy rain and strong winds in Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland from October 10 to 11.
In Nova Scotia, rain amounts were recorded from east to west as in Sydney, Nova Scotia, Sydney (Cape Breton Island), in Port Hawkesbury, in Chéticamp, Nova Scotia, Chéticamp, in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, in Kentville, and in Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Yarmouth. Heavy rains and strong winds caused flooding and dangerous conditions, particularly in the counties of Pictou, Antigonish, Guysborough and Cape Breton. Several roads were closed to heavy trucks, including Halifax Port Authority, Halifax Harbour bridges and the Confederation Bridge between New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island.
Newfoundland was even more affected with accumulations generally ranging from in the central, southern and western areas. Steady rain fell sometimes at a rate of per hour, and even per hour in Burgeo. A private station in that community recorded a total of , while the official station of the Gander International Airport signaled .
The rain caused numerous landslides and swollen rivers cut roads. The state of emergency was declared in Lewisporte, St. Alban's, Newfoundland and Labrador, St. Alban's and Little Burnt Bay. The town of St. Alban's, a community of about 1,200, was cut off from the surrounding communities when the main bridge in town was carried by the waters and a nearby community (Conne River) provided a boat to transport people to St. Alban's and out of the community. The highway to Burgeo, on the south coast of Newfoundland, was also flooded and had to be closed.
The winds of over also caused many fallen trees and electric power outages. The official maximum winds were recorded in Port aux Basques at and informally in Green Island, Fortune Bay, at . Insurance loss across Atlantic Canada were in excess of Canadian dollar, C$100 million (US$76 million).
Aftermath
Lesser Antilles
In Martinique, Électricité de France requested additional crews from Guadeloupe and French Guiana to help restore power. Members of the military and Forces françaises aux Antilles were deployed to assist in clearing debris from roadways. The St. Lucia Red Cross distributed non-food items to 270 people affected by the storm.Haiti
On October 4, the United States prepared the aircraft carrier, the hospital ship —which previously aided thousands in the wake of the 2010 Haiti earthquake—and the transport dock for relief operations in Haiti. and were later relieved by , along with the 24th Marine Expeditionary Unit. United States Southern Command also deployed 100 troops with 9 helicopters to the Cayman Islands to prepare for relief work. Initial estimates indicated at least 350,000 people were in need of assistance. The bridge between the south and Port-au-Prince was destroyed. As a result, aid agencies reported they were having difficulty getting around to the most damaged and storm-affected parts of Haiti. The commander of U.S. forces in the Caribbean reported that troops and 6 helicopters from Joint Task Force Bravo, Joint Task Force-Bravo had been deployed to Haiti for the aftermath, and were expected to arrive on October 6. These are expected to help with search-and-rescue missions as well as providing medical assistance. In addition to his, a one-star navy admiral will also travel to lead the task force involved in the operations. More than 300 military personnel will most likely travel to Haiti, with 300 Marines on board on the ships sent out for aid from the U.S. A number of aid agencies deployed to Haiti to help with the aftermath: * Action Aid reported that over 50,000 people were in immediate need of clean water and shelters. * World Nation also sent out helicopters, reporting difficulties and their concern about young children and food. They will be providing water and sanitation for over 50,000 people. * The UN's World Food Program arranged for enough food to feed up to 300,000 people for a month. A further 34 tonnes are ready in Miami to be used if needed. * UNICEF will be providing life-saving aid for 10,000 people. * UN's Food and Agricultural Organisation said it would be helping farmers rebuild their businesses by providing seeds. * The US Agency for International Development said it would provide $400,000 for aid to Jamaica and Haiti on October 3. * Red Cross launched a campaign to raise $9.6 million to provide water, shelter, and food for 50,000 people. They also sent a large number of local volunteers to the south.Cuba
The World Food Programme coordinated with the Government of Cuba to provide food to approximately 180,000 people in need across eastern provinces. The operation would span six months and cost US$4 million.Dominican Republic
The EU Caribbean Investment Facility and a €50 million loan from the European Investment Bank will finance the reconstruction of housing, but also other essential infrastructure lost including roads, bridges and urban infrastructure. Climate resilience will be improve through infrastructure being built to higher standards and through flood prevention and better use of land. Around 1,000 new house will be built for between 4 000 and 5 000 people with priority given to more economically vulnerable people.United States
 In Georgia, the Governor retracted previous evacuations later, emphasizing that their lives could not be endangered for those who chose not to leave. 1,000 members of the National Guard were deployed for help later.
In North Carolina, nearly 900 people had been rescued by boat crews by the morning of October 9. In April 2017, North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper requested $929 million in federal funds. The following month, the Trump administration denied more than 99 percent of this request and only provided $6.1 million to the state.
In Georgia, the Governor retracted previous evacuations later, emphasizing that their lives could not be endangered for those who chose not to leave. 1,000 members of the National Guard were deployed for help later.
In North Carolina, nearly 900 people had been rescued by boat crews by the morning of October 9. In April 2017, North Carolina Governor Roy Cooper requested $929 million in federal funds. The following month, the Trump administration denied more than 99 percent of this request and only provided $6.1 million to the state.
Retirement
On March 26, 2017, it was announced by the World Meteorological Organization that the name ''Matthew'' was retired, due to the extensive damage and loss of life it caused along its track, particularly in Haiti, Cuba, and the United States, and will never again be used to name an Atlantic hurricane. It was replaced with ''Martin'' for the 2022 Atlantic hurricane season.Response efforts
Direct Relief, an emergency response organization, delivered a large emergency medical aid airlift to Haiti. The organization used a 757 plane, donated by FedEx, that contained 16.7 tons of medicine and medical supplies.See also
* List of Cuba hurricanes * List of Florida hurricanes (2000–present) * List of North Carolina hurricanes (2000–present) *Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel was the deadliest, second costliest, and most intense hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm killed at least 469 people in Haiti before striking the United States near the border between North and Sout ...
– Took a similar track through the Caribbean in 1954, and struck North Carolina as a Category 4 hurricane.
* Hurricane David – Made landfall in the Dominican Republic as a Category 5 hurricane before skirting the eastern coast of Florida in 1979.
* Hurricane Tomas – Traced a slightly similar path in the Caribbean, but stayed out to sea rather than curving towards the United States after impacting Hispaniola in 2010.
* Hurricane Joaquin – Stalled in the Central Bahamas roughly a year before Matthew.
* Hurricane Dorian - Struck the northeastern Caribbean, devastated the northern Bahamas, and took a similar track up the southeastern United States in early September 2019.
Notes
References
External links
The NHC's advisory archive for Hurricane Matthew
* * *
EMSR186: Tropical Cyclone Matthew in Southeastern United States (delineation maps)
– Copernicus Emergency Management Service {{2016 Atlantic hurricane season buttons Hurricane Matthew, 2016 Atlantic hurricane season, Matthew 2016 in the Caribbean 2016 in Barbados 2016 in Cuba 2016 in Florida 2016 in Georgia (U.S. state) 2016 in Haiti 2016 in Martinique 2016 in North Carolina 2016 in Saint Lucia 2016 in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 2016 in South Carolina 2016 in Venezuela 2016 in Virginia 2016 natural disasters Category 5 Atlantic hurricanes, Matthew Hurricanes in the Windward Islands, Matthew Hurricanes in the Caribbean Natural disasters in Haiti Hurricanes in Barbados, Matthew Hurricanes in Dominica, Matthew Hurricanes in Martinique, Matthew Hurricanes in Saint Lucia, Matthew Hurricanes in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Matthew Hurricanes in Cuba, Matthew Hurricanes in Florida, Matthew Hurricanes in Georgia (U.S. state), Matthew Hurricanes in South Carolina, Matthew Hurricanes in North Carolina, Matthew Hurricanes in Virginia, Matthews Hurricanes in Haiti, Matthew Hurricanes in the ABC Islands, Matthew Retired Atlantic hurricanes, Matthew October 2016 events in North America October 2016 events in the United States September 2016 events in North America September 2016 events in the United States 2016 natural disasters in the United States Tropical cyclones in 2016, Matthew Hurricanes in the Bahamas, Matthew